26
Feb
Research Report: Green Roofs, Rainwater Harvesting & Green Approaches to Sustainable Hotel Development
Introduction
This research report aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of three key aspects in sustainable hotel development: green roofs, rainwater harvesting, and the adoption of green approaches in the hospitality industry. The information used for this report includes findings from various studies and research conducted in different locations, such as Ryomyong Street in Pyongyang, DPR Korea, Malaysia’s green hospitality industry, and high-density urban cities like Hong Kong.
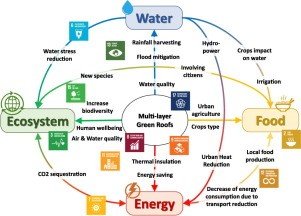
Rainwater Harvesting System on Buildings with Green Roofs
A feasibility study conducted on a rainwater harvesting system in buildings with green roofs and rooftop greenhouse in Ryomyong Street, Pyongyang, DPR Korea revealed several important findings. The annual average runoff coefficient of green roofs was determined to be 0.12, with monthly average runoff coefficients ranging from 0 (January to April and October to December) to 0.58 (July) over a period of 37 years. It was observed that the water demand for the greenhouse during December to June needed to be collected from other sources. However, the annual average reliability of the rainwater harvesting system increased from 91% (20 m3) to 99% (50 m3) when rainwater from the tank under the building was additionally supplied to the greenhouse. Furthermore, it was found that by using both the rooftop tank (20 m3) and the tank under the building (50 m3), the demand for the greenhouse could be fully met. The study also highlighted that an increase in catchment surface could lead to a substantial improvement in the reliability of the rainwater harvesting system. These research findings are valuable for local planners and authorities in improving water management and implementing sustainable urban development.
Green Approaches in Malaysia’s Green Hospitality Industry
A research study aimed to determine the rate of participation in green approaches in Malaysia’s green hospitality industry. In-depth interviews and observations were used as the methodology for this research. The study found that operators in the industry commonly adopt greener approaches in three areas: energy, waste, and water. However, there is less participation in indoor air quality, sustainable management of the site, renewable energy, and rainwater harvesting systems. This suggests that while progress has been made in certain areas, there is room for improvement in other aspects of sustainability within the industry.
Hydroponic Green Roof System for Urban Storm Water Management
A hydroponic green roof system (HGRS) was developed to reduce urban stormwater runoff and collect, treat, and reuse grey- and rainwater onsite in green buildings. The system treated greywater separately under three different hydraulic retention times (HRTs) of 4, 6, and 8 days, while simultaneously collecting rainwater and treating greywater under an HRT of 8 days. At an HRT of 8 days, significant removal efficiency of organic matter and anionic surfactants, as well as a decrease in turbidity, were observed. The average reduction in chemical oxygen demand (COD), five-day biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), anionic surfactants, and turbidity reached 81%, 97%, 88%, and 75% respectively. Microbial sequencing also demonstrated the presence of organisms capable of degrading anionic surfactants in the system. When the system collected rainwater and treated greywater simultaneously, the effluent showed lower concentrations of COD, BOD5, and anionic surfactants compared to when greywater was treated alone. This research highlights the effectiveness of hydroponic green roof systems in managing stormwater runoff and treating wastewater on-site.
Green Roofs for Urban Farming in High-Density Cities
Green roofs with urban farming have been recognized as effective techniques for Low Impact Development (LID) that contribute to environmental, social, and economic sustainability in urban cities. A research study focused on green roof urban farming for high-density urban cities like Hong Kong. The study examined the benefits and potential of rooftop urban farming, along with experiences from around the world. The characteristics and constraints of high-density urban cities were studied, specifically evaluating the situation in Hong Kong. The findings of this research can be useful for promoting sustainable buildings and environments in urban cities by integrating urban farming on green roofs.
Advantages of Green Roofing Systems for Sustainable Development
Green roofs provide numerous environmental benefits, including reducing flood risk, improving rainwater runoff quality, mitigating the urban heat island effect, saving building energy, and providing habitat for urban wildlife. Three roofing systems, including green roofs and agricultural roofing, have been identified as having sustainable advantages. These roofing systems can be designed to collect rainwater and reduce potable water usage. Green roofs, in particular, offer additional benefits such as reducing stormwater runoff, extending roof life, and enhancing thermal and sound insulation performance. Agriculture roofing combines the benefits of green roofs with the ability to grow food in urban areas, thereby reducing the carbon footprint. This paper confirms the societal and environmental benefits of these three roofing systems.
Assessing Green Roof Technology in Green Building Rating Systems
The development and utilization of green building rating systems are crucial for appraising existing and new green buildings. This paper explores the approach of assessing green building technologies based on rating systems to measure their performance and potential. It aims to clarify the role and position of green roof technology in various green building rating systems such as Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED), Green Building Index (GBI), and Singapore Building Construction Authority Green Mark. The research methodology involves analyzing the relevance and scoring performance of green roofs based on criteria stated in green building rating systems, including sustainable site planning and management, materials and resources, water efficiency, and innovation.
Conclusion
This research report highlights the importance of incorporating green roofs, rainwater harvesting systems, and green approaches in sustainable hotel development. The findings from various studies emphasize the potential benefits of these approaches in terms of water management, energy efficiency, stormwater runoff reduction, and overall environmental sustainability. The information presented in this report can be valuable for stakeholders, including local planners, authorities, and building developers, in making informed decisions to promote sustainable urban development and improve water management practices.
🙌💡 Join the Sustainable Investing Digest on LinkedIn to be a part of the solution! Subscribe to gain actionable insights on supporting sustainable practices in green roofs, sustainable hotels, global tourism and beyond. 📚💡 Don’t forget to share, repost, and comment upon this eye-opening research report to keep the momentum going! Let’s create a greener and more sustainable world together! 🌿🌏
🌟 Click here to subscribe: https://www.linkedin.com/build-relation/newsletter-follow?entityUrn=7053058780464345088 🌟